CSSnote1: CSS Basics
CSS Basics
What is CSS?
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)
- style sheet language(neither programming language nor markup language)
- to style HTML elements selectively
- need to be linked in
<head>of an HTML document like<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet">
Anatomy of a CSS ruleset
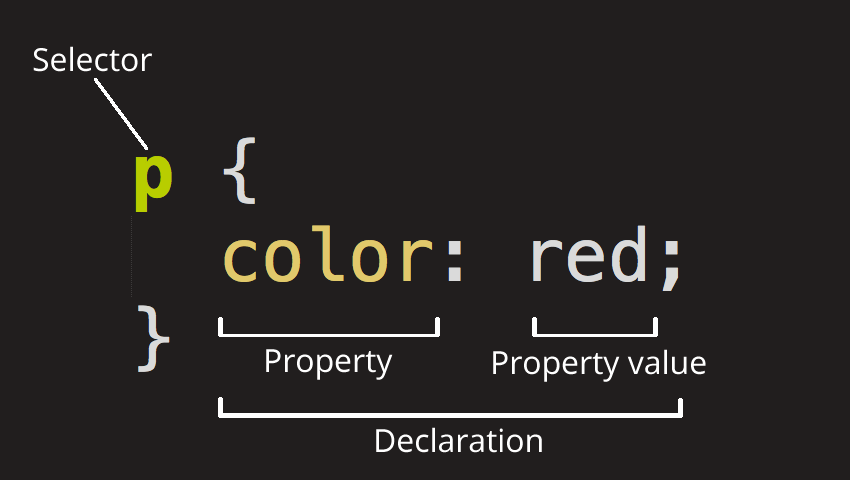
- Selector
- HTML element name at the start of the ruleset
- Declaration
- single rule like
color: red; - specifies element’s properties to style
- single rule like
- Properties
- HTML element’s property to affect
- Property value
- value for a given property
- Syntax of a ruleset
- Apart from the selector, each ruleset must be wrapped in
{} - Use
:to separate the property and its value - Use
;to separate each declaration - To select multiple elements as selector, use
,as separator1 2 3
p, li, h1 { color: red; }
- Apart from the selector, each ruleset must be wrapped in
Different types of selectors
| Selector name | What does it select | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Element selector | All HTML elements of the specified type. | pselects <p> |
| ID selector | The element with the specified ID. Each id value should be unique. | #my-idselects <p id="my-id"> |
| Class selector | The element(s) with the specified class. Classes can be duplicated. | .my-classselects <p class="my-class"> and <a class="my-class"> |
| Attribute selector | The element(s) with specified attribute. | img[src]selects <img src="myimage.png"> but not <img> |
| Pseudo-class selector | The specified element(s) but only when in the specified state. | a:hoverselects <a> but only when the mouse is hovering over the link |
이 외에도 많은 selector가 있음(MDN Selectors guide 참고)
Fonts and text
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
html {
font-size: 10px;
font-family: "Open Sans", sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 60px;
text-align: center;
}
p, li {
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 2;
letter-spacing: 1px;
}
- If there is a space in the font name, the font should be wrapped by double quotes
CSS: all about boxes
CSS layout is mostly based on the box model. Each box taking up space on your page has properties like:

padding: the space around the contentborder: the solid line outside the paddingmargin: the space around the outside of the borderwidth(of an element)background-color: the color behind an element’s content and paddingcolor: the color of an element’s content(usually text)text-shadow: for the text inside an elementdisplay: sets the display mode of an element
Example
CSS:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
html {
font-size: 10px;
font-family: 'Open Sans', sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 60px;
text-align: center;
}
p, li {
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 2;
letter-spacing: 1px;
}
html {
background-color: #00539F;
}
body {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #FF9500;
padding: 0 20px 20px 20px;
border: 5px solid black;
}
h1 {
margin: 0;
padding: 20px 0;
color: #00539F;
text-shadow: 3px 3px 1px black;
}
img {
display: block;
margin: 0 auto;
}
HTML:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My test page</title>
<link href="http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Mozilla is cool</h1>
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mdn/beginner-html-site-styled/gh-pages/images/firefox-icon.png" alt="The Firefox logo: a flaming fox surrounding the Earth.">
<p>At Mozilla, we’re a global community of</p>
<ul> <!-- changed to list in the tutorial -->
<li>technologists</li>
<li>thinkers</li>
<li>builders</li>
</ul>
<p>working together to keep the Internet alive and accessible, so people worldwide can be informed contributors and creators of the Web. We believe this act of human collaboration across an open platform is essential to individual growth and our collective future.</p>
<p>Read the <a href="https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/about/manifesto/">Mozilla Manifesto</a> to learn even more about the values and principles that guide the pursuit of our mission.</p>
</body>
</html>
shows an HTML document like below:
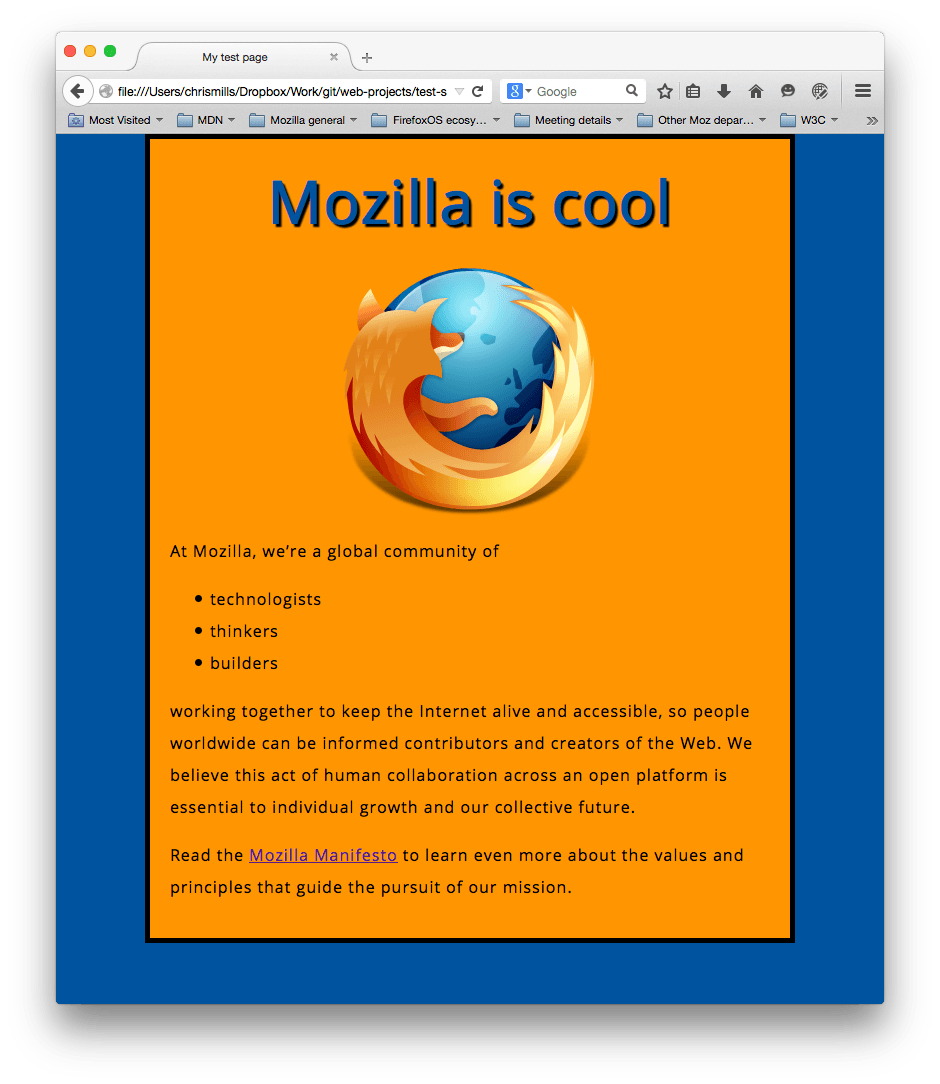
Explanation
marginandpadding- can have 1/2/3/4 values with several units(
em,%,px, …) orauto- 1 value : 4 sides
- 2 values : vertical / horizontal
- 3 values : top / horizontal / bottom
- 4 values : top / right / left / bottom
margincreates extra space around an element, whilepaddingcreates it within an element- browsers apply default styling to the
<h1>element -> there are margins in headings - top, bottom margins have no effect on non-replaced inline elements such as
<span>,<code>not headings(=block elements)
- can have 1/2/3/4 values with several units(
※ replaced elements : elements that css cannot change the content of the elements except its position, such as <iframe>, <img>, …
-
text-shadowhas 4 values(horizontal offset / vertical offset / blur radius / base color) -
displayproperty<img>is an inline element. To applymargin, it has to be treated as block element. -> Usedisplay: block;!- 웹페이지에서
<img>가<body>안에 있는 구조, 즉 이미지의 width가 600px 미만이라 가정한 상태임. 만약 600px 이상일 경우 body를 넘어서 표시됨. -> 이미지 너비를 미리 줄이거나 CSS에서 이미지 사이즈를 정의해줘야함!
css는 unknown canvas에 대해 웹페이지가 잘 읽힐 수 있도록 만들어짐 모든 css 코드들은 하나의 suggestion일 뿐이고 browser가 author, user, system을 종합해서 웹페이지를 보여줌 css 코드들은 브라우저가 이해가능한 것은 수용하고 그렇지 않은 것들은 무시하는 형태로 컴파일됨 따라서 backward compatible함

Leave a comment