HTMLnote2: Introduction to HTML
Introduction to HTML
Getting started with HTML
Semantic web
- HTML의 버전이 높아지면서 headings, figcaption 등 의미를 가지는 elements가 많아졌는데 이런 것들을 적절하게 사용하는 것
- SEO가 높아짐, crawler가 페이지 정보를 제대로 파악함
- 접근성(Accessibility)이 높아짐
Tags are case-insensitive!
Block-level vs. Inline elements
- Block-level elements
- have new line following/followed-by it
- are usually structural elements on the page(paragraphs, navigation menus, footers …)
- wouldn’t be nested inside an inline element
- Inline elements
- will not cause a new line to appear
- surround only small parts of the document’s content
- typically used with text
Boolean attributes
- can have only one value, which is generally the same as the attribute name
<input type="text" disabled="disabled">
※ shorthand :<input type="text" disabled>
Always include attribute quotes!
Whitespace in HTML
- 연속된 공백이나 줄바꿈문자는 HTML parser에 의해 하나의 공백으로 바뀜
-> 코드의 Readability를 위해 whitespace 사용(Indentation …)
Special characters in HTML
<,>,",',&: Character entity 사용!
| Literal character | Character reference equivalent |
|---|---|
< |
< |
> |
> |
" |
" |
' |
' |
& |
& |
e.g. <a href='http://www.example.com' title='Isn't this fun?'>A link to my example.</a>
나머지는 utf-8인코딩이면 그냥 사용해도됨
Comment
<!-- comment -->
Metadata in HTML(in <head>)
<title>
- metadata that represents the title of the overall HTML document(not the document’s content
<h1>)
<meta>
- element adding metadata to a document
- charset :
<meta charset="utf-8"> - name, content : name에 meta data type, content에 actual meta content 저장
- meta data type : author, description, keywords …
<meta name="author" content="siriyaoff">
<meta name="keywords" content="fill, in, your, keywords, here">- ignored by search engines because of spammers
※ Many<meta>features like keywords aren’t used any more
- Properietary creations
- Open Graph Data(Facebook’s)
<meta property="og:image" content="Image address"><meta property="og:description" content="Description"><meta property="og:title" content="Title">
- Twitter Cards(Twitter’s)
<meta name="twitter:title" content="Title">
- Open Graph Data(Facebook’s)
<link>
- favicon, CSS 등을 추가할 수 있음
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="CSSfile.css"> rel: 뒤에 나올 링크가 현재 페이지와 어떤 관련(relation)이 있는지 설명하는 attribute
-> SEO에 영향을 줌type: 링크된 외부 리소스의 미디어 타입 명시sizes: 링크된 외부 리소스의 크기 명시
<script>
- Javascript를 추가할 수 있음
<script src="jsfile.js" defer></script> - 소스파일을 링크할 수도 있지만 tag 사이에 코드를 바로 적을 수도 있음
- empty element가 아님!!
lang attribute in <html> element
- head 블록에 들어가지 않지만 문서 작성 초기에 해야하는것
- increases accessibility
<html lang="en-US"></html>로 문서가 사용하는 언어 명시
※<span lang="ko"></span>과 같이 특정 구역만 원하는 언어로 지정할 수 있음
Text fundamentals
The reasons we have to give structural markup to our content
- to give headings to users within a few seconds
- to increase SEO
- Accessibility
- to apply CSS, JavaScript effectively
list : ok to nest one list inside another one
- CSS 스타일로 마커 변경 가능
Emphasis and importance
- emphasis :
<em></em> - strong importance :
<strong></strong> - presentational elements :
<b></b>,<i></i>,<u></u>,<mark></mark>- to write bold, italics, underlined before CSS is fully supported
- lang과 같은 attribute 사용 가능 -> semantically appropriate하게 사용해야함
e.g.
The menu was a sea of exotic words like <i lang="uk-latn">vatrushka</i>, <i lang="id">nasi goreng</i> and <i lang="fr">soupe à l'oignon</i>.
Someday I'll learn how to <u style="text-decoration-line: underline; text-decoration-style: wavy;">spel</u> better.
Creating hyperlinks
<a>
- block-level element까지 link 가능
- attribute
titlecontains additional information about the link( = tooltip) - attribute
target:target="_blank"추가하면 새창에서 열림
URLs and paths
- URL(Uniform Resource Locator)s use paths to find files(URL ≠ path)
- Document fragments : a link to a specific part of an HTML document
idattribute를 이용해 fragment를 만들 수 있음
<h2 id="Mailing_address">Mailing address</h2>
<a href="#Mailing_address">mailing address</a>
과 같이 사용
- Absolute URL
- points to location defined by its absolute location on the web, including protocol and domain name
https://www.example.com/projects/index.html(디렉토리까지만 적으면 generally index.html을 의미) - alwasy point to the same location , no matter where it’s used
- points to location defined by its absolute location on the web, including protocol and domain name
- Relative URL
- points to location that is relative to the file you are linking from
project-brief.pdf(in same directory)
- points to location that is relative to the file you are linking from
Clear link wording
- We need to make our links accessible to all readers
- Don’t repeat the URL as part of the link text
- Don’t say “link” or “links to” in the link text
- Keep your link as short as possible
- Minimize instances where multiple copies of the same text are liked to different places(“click here”s)
Use relative links wherever possible
- easier code, more efficient performance(use same server to look up the file in the link)
Linking to non-HTML resources - leave clear signposts
<a href="large-report.pdf">Download the sales report (PDF, 10MB)</a><a href="https://www.example.com/car-game">Play the car game (requires Flash)</a>downloadattribute : provide a default save name<a href="div1timetable.pdf" download="timetable.pdf">Timetable for div.1 (English, US)</a>
모든 페이지들의 링크를 모아서 navigation menu를 만들 수도 있음(모든 페이지에 자신의 링크를 빼고 넣어놓으면 같은 페이지같은 느낌 줌)
E-mail links
mailto:URL scheme 사용
<a href="mailto:nowhere@mozilla.org">Send email to nowhere</a>mailto:뒤에 recipient의 메일주소를 생략하면 메일 쓰는 창만 열림 -> share 기능- recipient 이외에도 mail header fields를 URL에 추가할 수 있음
cc: Carbon Copybcc: Blind Carbon Copysubject: Email subjectbody: Email body- main URL과 field values를 분리할 때는
?사용, field끼리 분리할 때는&사용, field values끼리 분리할 때는;사용
e.g.
"mailto:nowhere@mozilla.org?cc=name2@rapidtables.com&bcc=name3@rapidtables.com;name4@rapidtables.com&subject=The%20subject%20of%20the%20email&body=The%20body%20of%20the%20email"
Advanced text formatting
Description lists(dictionary list)
<dl>: description list, wrap whole list like<ol><dt>: description term, wrap each term<dd>: description definition, wrap each description- It is permitted to have a single term with multiple descriptions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<dl>
<dt>term1</dt>
<dd>description1</dd>
<dt>term2</dt>
<dd>description2</dd>
<dd>description3</dd>
</dl>
is equivalent to
1
2
3
4
5
term1
description1
term2
description2
description3
Quotations
Blockquotes
<blockquote>이용citeattribute로 출처 남길 수 있음- will be rendered as indednted paragraph by browser default styling
Inline quotations
<q>이용- will be rendered as normal text put in quotes by browser default styling
Citations
<cite>이용- italicize 이외의 기능은 없음 -> 인용문에는 quotation elements with
citeattribute, 출처에는<a>,<cite>elements 이용해서 표시해줘야함
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<p>Here below is a blockquote...</p>
<blockquote cite="https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/blockquote">
<p>The <strong>HTML <code><blockquote></code> Element</strong> (or
<em>HTML Block Quotation Element</em>) indicates that the enclosed text is an extended quotation.</p>
</blockquote>
<!-- Inline quotation and citation -->
<p>According to the <q><a href="#blockquote"><cite>MDN blockquote page</cite></a></q>:</p>
Abbreviations
<abbr>이용<acronym>도 있지만<abbr>과 겹쳐서 잘 쓰지 않음titleattribute의 attribute value가 tooltip으로 표시됨
<p>We use <abbr title="Hypertext Markup Language">HTML</abbr> to structure our web documents.</p>
1
2
3
4
5
6
※ 알쓸신잡(abbreviation, acronym, initialism) ※
- abbreviation : any shortend or contracted form of a word or phrase(Rly, ex, ...)
- acronym : a specific type of abbreviation formed the first letters of a multi-word term(OPEC, THAAD, ...)
- initialism : a type of acronym but usually pronounced by saying each letter of the acronym(IDK, ATM, ...)
- 즉 initialism ∈ acronym ∈ abbreviation
Contact details
<address>이용- namecard느낌, italicize 이외의 기능은 없음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
<address>
<p>
Chris Mills<br>
Manchester<br>
The Grim North<br>
UK
</p>
<ul>
<li>Tel: 01234 567 890</li>
<li>Email: me@grim-north.co.uk</li>
</ul>
</address>
Superscript and subscript
<sup>,<sub>이용
<p>If x<sup>2</sup> is 9, x must equal 3 or -3.</p>
Representing computer code
<pre>: For retaining whitespace(preformatted text)<code>: For marking up generic pieces of computer code<var>: For specially marking up variable names<kbd>: For marking up keyboard and any other types of input entered<samp>: For marking up the output of a computer program- Though they are all same after rendering, they has to be written according to the intentions made
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
<pre><code>var para = document.querySelector('p');
para.onclick = function() {
alert('Owww, stop poking me!');
}</code></pre>
<p>You shouldn't use presentational elements like <code><font></code> and <code><center></code>.</p>
<p>In the above JavaScript example, <var>para</var> represents a paragraph element.</p>
<p>Select all the text with <kbd>Ctrl</kbd>/<kbd>Cmd</kbd> + <kbd>A</kbd>.</p>
<pre>$ <kbd>ping mozilla.org</kbd>
<samp>PING mozilla.org (63.245.215.20): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 63.245.215.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=40 time=158.233 ms</samp></pre>
Times and dates
<time>이용datetimeattribute로 시간 저장
<time datetime="2016-01-20">20 Jan. 2016</time>
Document and website structure
Basic sections of a document(in the <body>)
header
- a big strip across the top with a big heading, logo, and perhaps a tagline
- stays the same from one webpage to another
navigation bar
- links to the site’s main sections
- represented by menu buttons, links, or tabs
- remains consistent from one webpage to another
- considered to be part of the header rather than an individual component(not requirement, two separate is better for accessibility)
main content
- a big area in the center contains most of the unique content of a given webpage
sidebar
- peripheral info, links, quotes, ads, …
- contextual to what is contained in the main content
footer
- a strip across the bottom of the page that generally contains copyright notices, contact info
- sometimes used for SEO purposes, by providing links for quick access to popular content
“typical website”
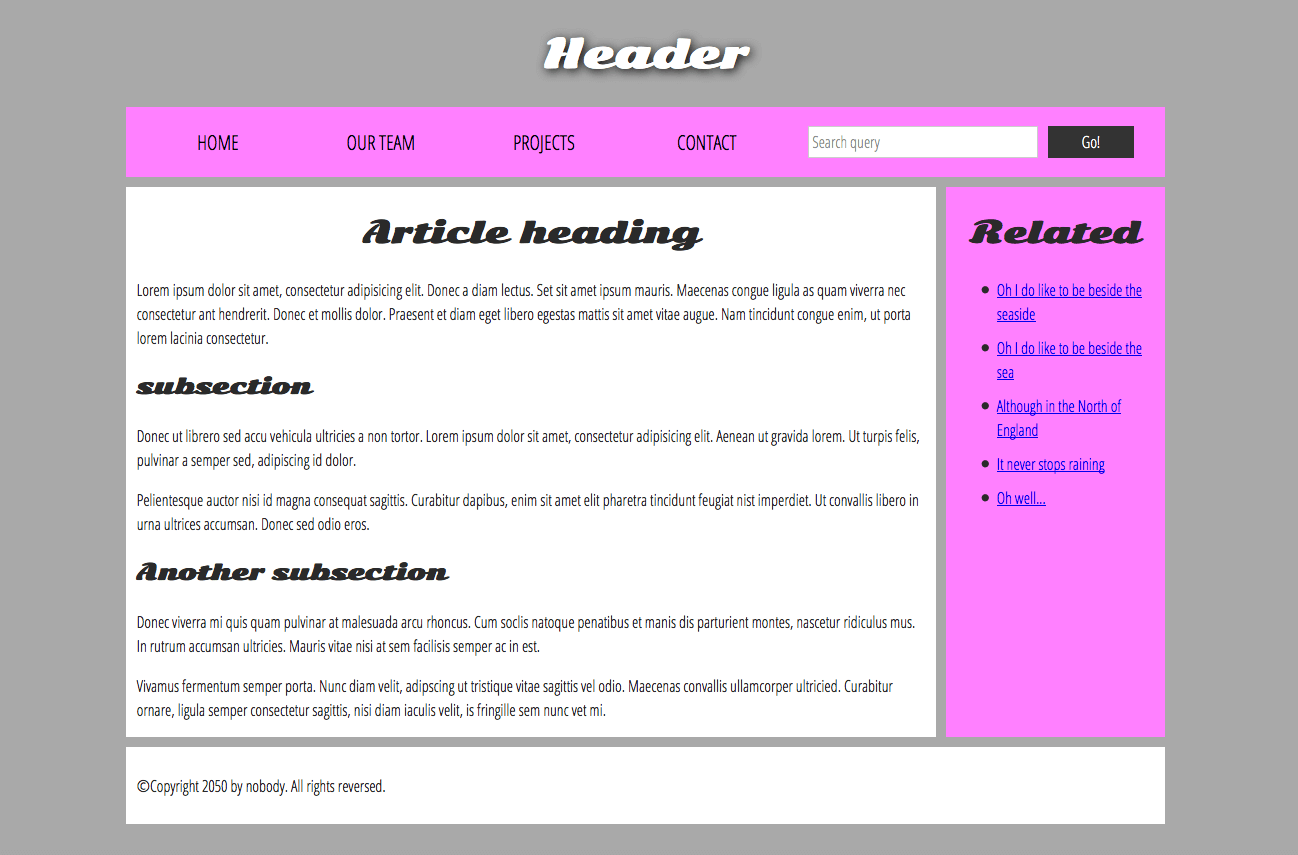
HTML for structuring content+layout elements in more detail
- we need to respect semantics and use the right element for the right job
<header>
- represents a group of introductory content
<header>in the<body>: global header of a webpage<header>in the<article>or<section>: specific header for that section
<nav>
- contains the main navigation functionality for the page
<main>
- for content unique to this page
- only once per page, directly inside
<body> - shouldn’t be nested within other elements
<article>
- encloses a block of related content(e.g., a single blog post)
<section>
- similar to
<article> - grouping a single part of the page that constitutes one single piece of functionality(e.g., a mini map, a set of article headlines and summaries)
<section>,<article>은 서로 포함될 수 있음
<aside>
- sidebar, often placed inside
<main> - containes content can provide additional information indirectly related to it(glossary entries, author biography, related links, …)
<footer>
- represents a group of end content for a page
Non-semantic wrappers
- group a set of elements together to affect them all as a single entity with some CSS or JavaScript
- have to be used preferably with a suitable
classattribute <span>- inline non-semantic element
<span class="editor-note">[Editor's note: ...]</span>
- inline non-semantic element
<div>- block level non-semantic element
<div class="shopping-cart">SOME HTML CODES</div> <aside>가 아님(현재 페이지의 main content와 관련되어있지 않고 어느 페이지에서든 볼 수 있어야함, main content가 아니기 때문에<section>에 맞지도 않음)- heading을 넣어서 accessibility를 높일 수도 있음
- Try to reduce usage to the minimum
- block level element의 경우 background att로 배경 설정 가능
- block level non-semantic element
Line breaks and horizontal rules
<br>: creates a line breaks<hr>: creates a horizontal rule denotes a thematic change
Planning a simple website
- Note down common things to every page(header(title, logo), footer(contact details, copyright notice, …))
- Draw a rought sketch of structure of each page(blocks)
- Brainstorm all the other content
- Sort all these content items into groups appropriately(theme, purpose, …)
- Sketch a rought sitemap(Home page, Buy, Specials, Country-specific info, …)
Debugging HTML
-
HTML is not compiled into a different form before the browser parses it and shows the result(it is interpreted, not compiled)
-
Permissive code - HTML itself doesn’t suffer from syntax errors because browsers parse it permissively(interpreted even if there are syntax errors)
-
HTML codes can be checked in Markup Validation Service
Assessment01: Marking up a letter
-
class, style같은 attribute들은 global attributes로 웬만한 element에는 다 포함되어있다
-
list elements는
<p>안에 nested될 수 없다<p>는 content model이 phrasing content(=inline elements)기 때문
Assessment02: Structuring a page of content
-
<header>는 content model(permitted content)가 flow content이다 -
<header>과<footer>는<body>안에 포함되지만 용도에 따라<main>에 포함될 수도 아닐수도 있다
Anatomy of assessment02
- head : metadata
- body
- header : global title, logo, navigation bar
- main : article, aside
- footer : copyright, contact info

Leave a comment