HttpServer in Java
보통 아래와 같은 순서로 HttpServer를 사용해 서버를 개설함
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
String uri = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 5678;
HttpServer server = HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress(uri, port), 0);
server.createContext("/", new rootcontroller());
server.createContext("/sum", new sumcontroller());
server.setExecutor(null);
server.start();
System.out.println("Server started on port " + port);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Server connection failed");
}
}
HttpServer-HttpServerProvider-DefaultHttpServerProvider-HttpServerImpl-ServerImpl순서로 제어 흐름이 넘어가면서ServerImpl에서 직접적으로 서버가 개설됨- 글 가장 아래에 자세한 클래스 관계 및 다이어그램에 정리함
server.createContext(String path, HttpHandler handler):path,handler를 매핑한HttpContextImpl인스턴스를 생성하고ServerImpl의 필드인ContextList contexts에 추가함server.setExecutor(null): 스레드 관련 설정null로 설정하면server.start()를 실행한 스레드만을 사용하는 default implementation이 사용됨
HttpServer 와 관련된 자세한 클래스 관계 및 다이어그램
InetSocketAddress
SocketAddress클래스를 상속받음String hostname,InetAddress addr,int port를 필드로 가짐InetAddress: IP 주소를 저장하는 클래 스InetAddressHolder클래스로 IP 정보를 저장함- hostname, address, family 등
- 생성자
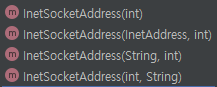
InetSocketAddress(int port):addr은InetAddress.anyLocalAddress()로 설정InetSocketAddress(InetAddress addr, int port):hostname은null로 저장InetSocketAddress(String hostname, int port):addr은InetAddress.getByName(hostname)으로 설정
HttpServer
HttpServer.create(InetSocketAddress addr, int backlog)1 2 3 4 5 6
public static HttpServer create ( InetSocketAddress addr, int backlog ) throws IOException { HttpServerProvider provider = HttpServerProvider.provider(); return provider.createHttpServer (addr, backlog); }
HttpServerProvider.provider():DefaultHttpServerProvider객체를 생성하고 리턴함HttpServerProvider는 추상 클래스임
backlog: 서버와 연결 가능한 최대 소켓 수
DefaultHttpServerProvider
HttpServerProvider추상 클래스의 구현체createHttpServer메소드1 2 3
public HttpServer createHttpServer (InetSocketAddress addr, int backlog) throws IOException { return new HttpServerImpl (addr, backlog); }
HttpServerImpl
Httpserver클래스를 상속받음ServerImpl의 wrapper- 생성자
1 2 3 4 5
HttpServerImpl ( InetSocketAddress addr, int backlog ) throws IOException { server = new ServerImpl (this, "http", addr, backlog); }
ServerImpl
TimeSourceinterface의 구현체-
생성자
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
ServerImpl ( HttpServer wrapper, String protocol, InetSocketAddress addr, int backlog ) throws IOException { this.protocol = protocol; this.wrapper = wrapper; this.logger = System.getLogger ("com.sun.net.httpserver"); ServerConfig.checkLegacyProperties (logger); https = protocol.equalsIgnoreCase ("https"); this.address = addr; contexts = new ContextList(); schan = ServerSocketChannel.open(); if (addr != null) { ServerSocket socket = schan.socket(); socket.bind (addr, backlog); bound = true; } selector = Selector.open (); schan.configureBlocking (false); listenerKey = schan.register (selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); dispatcher = new Dispatcher(); idleConnections = Collections.synchronizedSet (new HashSet<HttpConnection>()); allConnections = Collections.synchronizedSet (new HashSet<HttpConnection>()); reqConnections = Collections.synchronizedSet (new HashSet<HttpConnection>()); rspConnections = Collections.synchronizedSet (new HashSet<HttpConnection>()); time = System.currentTimeMillis(); timer = new Timer ("server-timer", true); timer.schedule (new ServerTimerTask(), CLOCK_TICK, CLOCK_TICK); if (timer1Enabled) { timer1 = new Timer ("server-timer1", true); timer1.schedule (new ServerTimerTask1(),TIMER_MILLIS,TIMER_MILLIS); logger.log (Level.DEBUG, "HttpServer timer1 enabled period in ms: ", TIMER_MILLIS); logger.log (Level.DEBUG, "MAX_REQ_TIME: "+MAX_REQ_TIME); logger.log (Level.DEBUG, "MAX_RSP_TIME: "+MAX_RSP_TIME); } events = new LinkedList<Event>(); logger.log (Level.DEBUG, "HttpServer created "+protocol+" "+ addr); }
- 실제 서버 초기화를 담당함
ServerSocket객체를 통해 서버와의 소켓 연결도 초기화함socket.bind에서backlog<1일 경우50으로 설정됨
HttpContextImpl
HttpContext추상 클래스의 구현체ServerImpl객체의 메소드인serverImpl.createContext(String path, Httphandler handler)에서 생성됨1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public synchronized HttpContextImpl createContext (String path, HttpHandler handler) { if (handler == null || path == null) { throw new NullPointerException ("null handler, or path parameter"); } HttpContextImpl context = new HttpContextImpl (protocol, path, handler, this); contexts.add (context); logger.log (Level.DEBUG, "context created: " + path); return context; }
-
생성자
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
HttpContextImpl (String protocol, String path, HttpHandler cb, ServerImpl server) { if (path == null || protocol == null || path.length() < 1 || path.charAt(0) != '/') { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal value for path or protocol"); } this.protocol = protocol.toLowerCase(); this.path = path; if (!this.protocol.equals ("http") && !this.protocol.equals ("https")) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal value for protocol"); } this.handler = cb; this.server = server; authfilter = new AuthFilter(null); sfilters.add (authfilter); }
- 의문점
- create()에서 HttpServer-HttpServerProvider-DefaultHttpServerProvider-HttpServerImpl으로 돌려서 인스턴스를 생성하는데 HttpServer-HttpServerImpl으로 생성하는 거랑 다른 점
- 아마 HttpServerProvider의 다른 추상 메소드들의 도메인 때문에 분할한 듯
- create()에서 HttpServer-HttpServerProvider-DefaultHttpServerProvider-HttpServerImpl으로 돌려서 인스턴스를 생성하는데 HttpServer-HttpServerImpl으로 생성하는 거랑 다른 점


Leave a comment